Red Light Therapy for Testosterone
From a biological standpoint, testosterone is the hormone that defines many masculine characteristics, though it is also crucial for women’s overall health. Testosterone levels naturally surge during puberty and start to decline around the age of 30. While a gradual reduction is a normal aspect of aging, this decrease can lead to unwanted side effects if levels fall too low. Utilizing red light therapy for testosterone could help the body restore optimal testosterone levels, thereby revitalizing energy, drive, and overall well-being.
Why You Might Consider Boosting Your Testosterone
Testosterone is the key sex hormone that plays a crucial role in male sexual performance and reproductive capabilities. It also impacts secondary traits such as a deeper voice, facial hair growth, and increased muscle and bone density.
Low testosterone can disrupt both primary sexual function and secondary characteristics, potentially leading to emotional and psychological stress.
For women, testosterone is also an essential element of overall well-being, supporting bone strength, reproductive health, cognitive function, and physical vitality. Women produce small amounts of testosterone in the ovaries, adrenal glands, fat cells, and skin.
Like men, women can also experience symptoms related to low testosterone, which, although less discussed, can still present challenges.
The American Urological Association notes that a gradual decline in testosterone production is a normal part of aging. However, the organization estimates that around 2 out of every 100 men experience abnormally low testosterone, a condition known as Low T.
Even if you haven’t been diagnosed with Low T, you may wish to increase your body’s natural ability to produce testosterone if you’re having troubles with:
- Reduced muscle mass and weight gain (particularly excess belly fat);
- Low energy levels, diminished strength, poor endurance, and poor physical performance;
- Low sex drive and poor sexual satisfaction;
- Reduced bone mass, which can lead to osteoporosis and increased risk of fractures;
- Erectile dysfunction;
- Insomnia and sleep apnea, leading to increased daytime fatigue;
- Mood swings, irritability, and depression;
- Lack of mental focus/brain fog;
- Hot flashes: Low T is one cause of hot flashes in men with andropause (male menopause);
- Infertility: Low T can lead to testicular shrinkage and increased softness of the scrotum, both of which could be an indication of reduced sperm counts.
Low testosterone could be a contributing factor in these symptoms, but other factors are often involved as well. Many could have causes other than Low T, such as stress, poor lifestyle habits, and chronic underlying conditions. Therefore, it’s important to consult a doctor before trying to increase your testosterone levels on your own.
If your symptoms are mild, you may not feel the need to do anything about it right now. But if you’ve been feeling older than your years, you don’t have the sex drive you once had, and you lack your former energy levels, there are ways to boost testosterone naturally and safely.
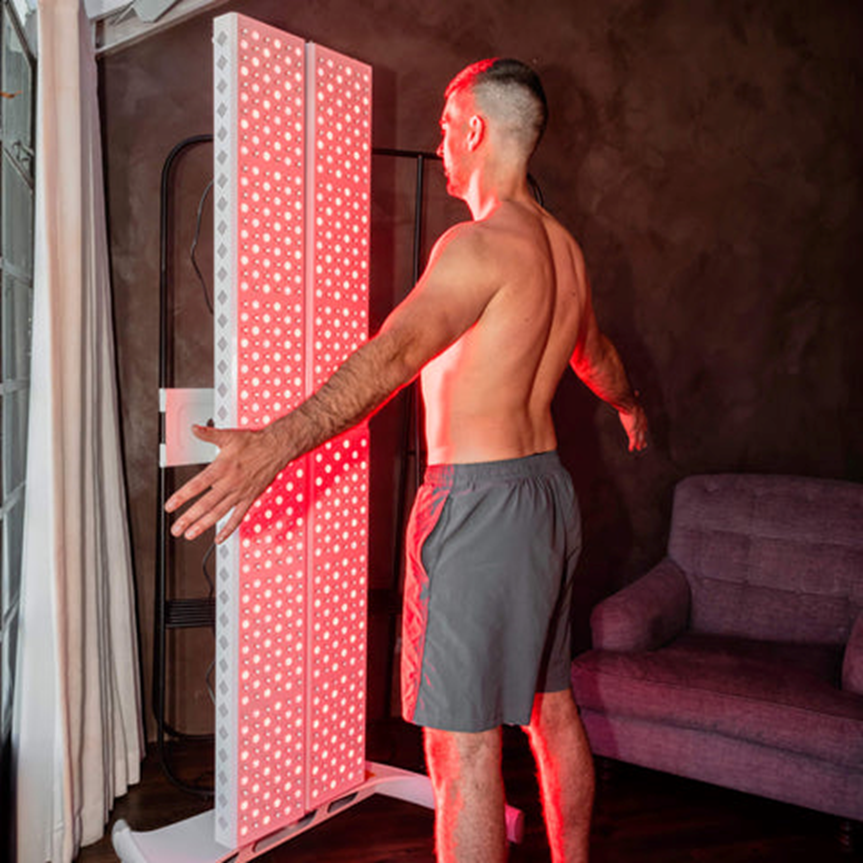

Red Light Therapy for Testosterone
Studies indicate a direct relationship between natural sunlight exposure and the body’s capacity to produce testosterone. Humans are highly sensitive to light, and increased light exposure has been shown to stimulate beneficial biological processes within the body. The key lies in utilizing the appropriate types of light.
Natural bright light from sunlight has been employed for centuries to address a wide range of physical and psychological conditions. Today, bright light can be administered through artificial full-spectrum lighting.
Bright light therapy is commonly used to treat seasonal depression, known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD), as well as chronic (non-seasonal) depression, postpartum depression, acne, various chronic skin issues, pain, and to support the immune system.
According to the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, low libido affects nearly 25 percent of men over age 40. During a 2016 study by the group, exposure to bright light increased sexual desire and satisfaction, as well as testosterone levels. Research had previously discovered seasonal fluctuations in libido, which prompted this study.
The issue with natural sunlight or full-spectrum bright light devices is that, along with the beneficial wavelengths, sunlight also emits harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is known to cause premature skin aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Blue light has been effectively used for treating acne as it is known to kill acne-causing bacteria on the skin. On the other hand, red light therapy utilizes specific wavelengths, particularly red light in the range of 630 to 660 nanometers (nm), and near-infrared (NIR) light ranging from 810 to 850 nm.
These wavelengths have been extensively studied in relation to a variety of health conditions. Although clinical trials on the direct impact of red and NIR light on testosterone are still in the early stages, the positive effects on both male and female reproductive systems suggest its potential to enhance testosterone levels.
Red light therapy, also known as low-level light therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation (PBM), falls within what is referred to as the “therapeutic window” of light.
How Red Light Therapy Can Naturally Boost Testosterone
There are several mechanisms by which red light therapy can support your body in naturally boosting testosterone levels and potentially reversing testosterone abnormalities.
A 2013 study by researchers from Korea involved stimulating increased production of testosterone in male rats after treating them with a combination of red and NIR light, suggesting that red light could be an alternative treatment modality to conventional testosterone replacement therapy — which, even though it’s effective, can carry many unwanted side effects.
Here’s how red-light therapy works to treat testosterone problems.
Increased Energy Production in the Cells
In men, red light stimulates energy production in the Leydig cells, which are the cells responsible for producing testosterone. Enhanced energy production in Leydig cells is believed to help naturally increase testosterone production and restore age-appropriate (or better) testosterone levels.
It’s not just the Leydig cells that benefit from increased energy production. Red light therapy has numerous benefits, the most important being the positive interaction between light photons and the mitochondria, which are the energy centers within cells.
But why is it important to boost cellular energy? Here’s where things get interesting because treating the cause of low cellular energy could potentially hold the answer to reversing Low T.
The mitochondria’s job is to convert raw materials into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary fuel for all the cells in the body. When cells are energized, they function optimally, repair themselves, and replicate.
But when mitochondria aren’t able to produce ATP (known as mitochondrial dysfunction), the cells suffer — and low-energy cells can’t do their jobs properly. In the case of the Leydig cells, if they don’t have enough energy, they may prioritize survival over their specialized functions.
Therefore, reversing mitochondrial dysfunction could hold the answer to many chronic health problems, including Low T.
A study published in a 2019 issue of Review of Optometry found that red light may have therapeutic value and even reverse the damage of mitochondrial function. Although this study was focused on eye care, the researchers’ discovery about red light and mitochondrial function was profound.
During an older University of California San Diego study (published in 2008), researchers confirmed that treatment with red and NIR light increased ATP production by mitochondria. In addition, the treatment positively influenced cellular homeostasis (optimal functioning under normal circumstances), as well as cell proliferation.
What this means for you: red light therapy (which includes both red and NIR wavelengths) can work from the inside-out, on a cellular level, to boost cellular performance. This could potentially have a ripple effect that normalizes the production of sex hormones, including testosterone.
As a side note, if you click on the links to read these studies, you may notice red light therapy referred to as “low-level laser therapy.” That’s because, in many clinical trials, researchers use lasers to deliver the red light. That is starting to change, however, as an increasing number of researchers are using LED devices. The wavelengths studied are the same; only the delivery is slightly different, with low-level laser therapy using “cold” lasers as opposed to a light-emitting diode (LED) light therapy device.
Reduced Inflammation
One of the potential causes of mitochondrial dysfunction is chronic inflammation. Here’s another area where red light therapy “shines.”
Dr. Michael Hamblin, one of the world’s top experts in red light therapy, wrote a paper in 2017 titled “Mechanisms and Applications of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Photobiomodulation.” In this paper, Hamblin outlines what is currently known about the effects of red light on chronic inflammation.
As he stated: “One of the most reproducible effects of PBM is an overall reduction in inflammation,” which suggests that red light therapy could reduce the inflammation that’s at the root of mitochondrial dysfunction.
Along with reducing inflammation, red light therapy may help the cells responsible for testosterone production (and in women, those responsible for producing female sex hormones) repair damage due to inflammation, and redirect their resources to their specialized functions.
Increased Circulation
A 2017 study focused on the effects of diabetic peripheral artery disease found that red light stimulated vasodilation in both healthy and diabetic blood vessels. This holds promise in treating not only diabetic vascular disease but any condition where poor circulation could be a contributing cause — such as erectile dysfunction.
Red light therapy has been shown to increase the production of endothelial cells, which make up the tiny capillaries that deliver blood and lymph throughout the body’s extremities, including the testicles.
Red light also appears to have a protective effect on red blood cells that are under stress due to oxidative stress, according to a 2018 study published in the Frontiers of Physiology.
What does this mean for you? Increasing circulation brings nutrients and oxygen to cells, and removes waste and toxins. The result is improved cellular health and improved functioning.
Erectile dysfunction is often due to poor blood flow, so this could be a welcome solution if you’re suffering from ED or low sex drive as a result of sexual performance fears. Increasing circulation could be one way to boost sexual satisfaction.
While more studies are needed on the specific effects of red light therapy treatments on increasing testosterone levels, a huge body of peer-reviewed research shows promise in using red light to boost the body’s self-healing mechanisms, particularly when it comes to aging.
Improved Moods and Reduced Anxiety
Major depression and anxiety can result from Low T because of the lifestyle and relationship challenges that often accompany the condition. In this groundbreaking study by Harvard Medical School researchers, red light therapy successfully treated depression and anxiety.
Participants included ten patients with severe depression, nine of whom also had anxiety. After several treatments with near-infrared light, the patients experienced significant reductions in both depression and anxiety, without side effects.
Red light could potentially be used to treat depression and anxiety, thereby reducing stress. This is good news since stress is known to cause disturbances in the endocrine system, which governs hormone production and therefore testosterone levels.
Specific Benefits of Increased Testosterone Production — and How Red Light Can Help
Increasing the body’s natural testosterone production could have a positive ripple effect on your health. But whether the following symptoms are related to Low T or not, red light can help you find relief.
You may experience greater athletic performance (both men and women) as you restore normal physical energy and as you regain muscle mass and lose excess fat. You can also boost athletic performance by using red light therapy before and after exercise, to stimulate the muscles for exercise, recover faster, and help prevent injury. According to a 2016 clinical review co-authored by Hamblin, red light therapy may even give you an unfair advantage in sports.
You may experience improved mental and emotional functioning. The previously cited study relating to depression and anxiety is important: shining NIR light onto the forehead for a short time each day could help reduce stress-induced mental fog.
You may experience less severe menopause/andropause symptoms, including hot flashes. Red light therapy has been used successfully to treat thyroid issues. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid functioning) has been linked to more severe menopause symptoms. According to a 2007 study by Egyptian researchers, by treating hypothyroidism, these symptoms can ease up.
In 2018, a study by Brazilian researchers confirmed that red/NIR light has long-term positive effects on thyroid health.
Boosting Your Testosterone Naturally with Red Light Therapy
Whether you’re male or female, you don’t have to suffer from low testosterone. You can increase testosterone production naturally, which could solve many of your physiological challenges including poor sexual health, low sex drive, low energy, lost muscle mass and weight gain, and mental fog.
